Amid rising energy costs and sustainability concerns, many homeowners are looking for ways to save money on their monthly bills while also reducing their carbon footprint. One of the best ways to achieve these goals is through geothermal heating and cooling.
Ground-source thermal energy systems have been around for decades but have gained in popularity in recent years, given the advantages they offer over traditional HVAC systems.
How Geothermal Heating and Cooling Saves Energy
Temperatures on Earth’s surface vary widely. Depending on where you live, it could get extremely hot during summer and super cold during winter. This variance also occurs daily as noontime is hotter while evenings are cooler.
Conventional HVAC systems use outside air temperature to regulate indoor conditions using electricity. However, because of the wide variance, these systems tend to work harder to produce heat during cold weather and cool air during summer.
This inefficiency is why energy costs are rising. According to EnergyStar, the average homeowner spends around $1,900 annually on energy bills, with nearly 50% of that going to heating and cooling.
On the other hand, geothermal heating and cooling systems harness the relatively stable subterranean temperatures to regulate indoor requirements. At 30 feet below the Earth’s surface, temperatures oscillate between 50-59 degrees Fahrenheit year-round, providing a more viable and efficient heat exchange than above surface conditions.
In this way, geothermal heat pumps consume less energy to achieve desired indoor temperatures even as the seasons change. According to the U.S. Department of Energy, these systems can reduce power usage and emissions by up to 72% compared to standard air-conditioners.
Cost Savings
Geothermal heat pumps use significantly less electricity than conventional heating or cooling systems, lowering utility bills. After installation, homeowners can expect cost savings ranging from 25% to 50% than traditional fossil fuel HVAC systems.
Existing homes and new construction projects that install geothermal heating and cooling solutions can also qualify for federal energy efficiency tax credit. This program awards up to 30% of the cost of installing an ENERGY STAR-certified ground-source system and is available through the end of 2034. Principal residences and second homes are eligible for this tax credit, and may also qualify for state and local incentives, resulting in even more savings.
On top of that, low and middle income households may also benefit from the High-Efficiency Electric Home Rebate Act, which awards up to $8,000 rebate for heat pump HVAC systems.
Also Read: What Are the Best Ways to Save Energy at Home?
Longevity
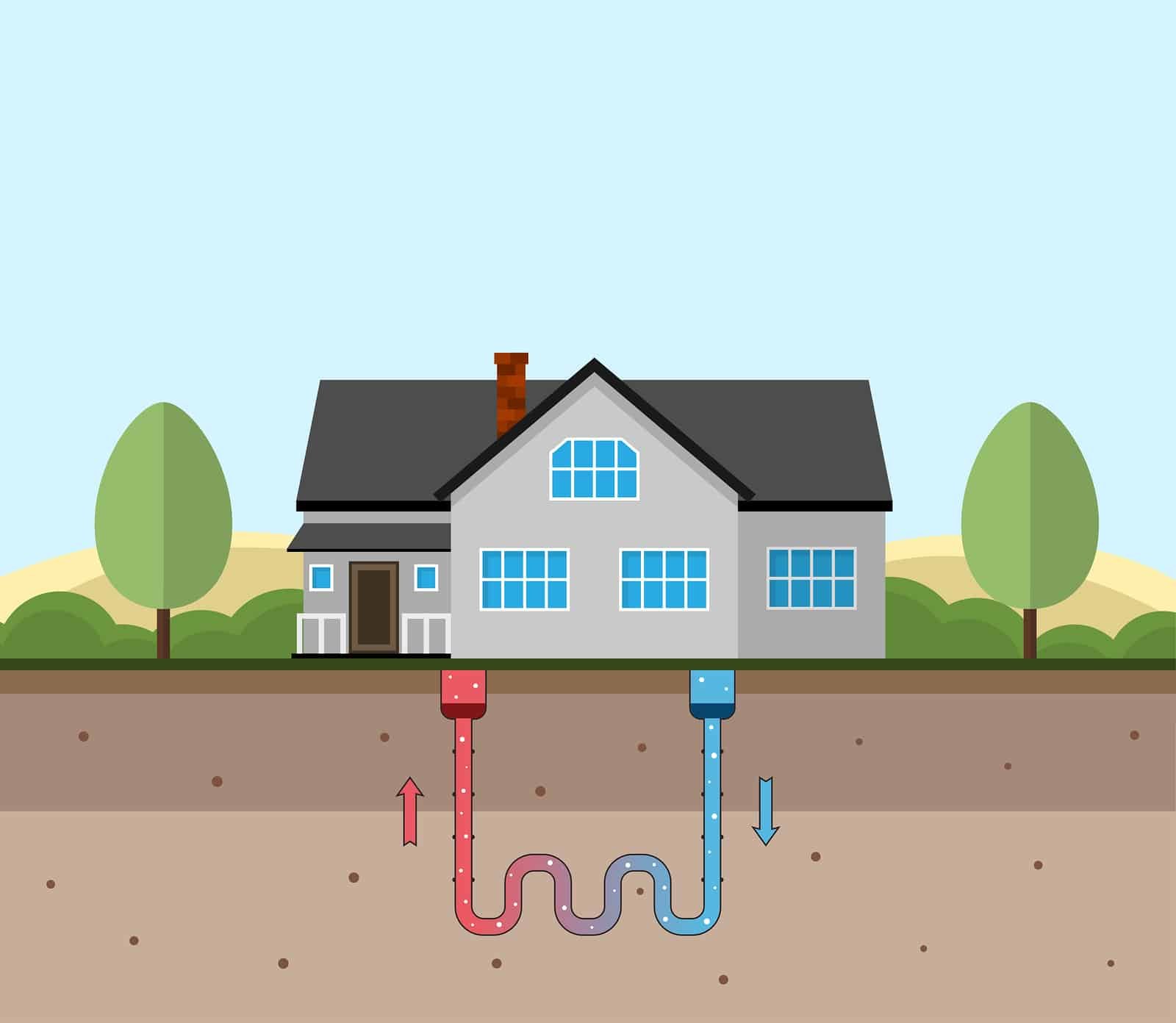
Another great benefit of geothermal heat pumps is the long service life. Because they are buried underground, these systems are safe from weather exposure and tampering. As a result, the ground heat exchanger or loop system has a life expectancy of over 50 years, while the indoor components have an average life span of 24 years. This is more than enough time to recoup the installation costs.
There are also fewer moving components, which means lower maintenance costs. Additionally, as the adoption of these systems increases, so will the innovation behind them, potentially improving their longevity and efficiency.
Environmental Benefits
One of the biggest drawbacks of conventional HVAC systems is the reliance on electricity from fossil fuels. This leads to climbing rates of greenhouse gas emissions, in turn worsening the effects of climate change.
Geothermal pumps don’t rely on burning fuels to produce heating and cooling energy. Instead, these systems tap into the perpetually renewable energy from underground reservoirs. Furthermore, this source is always available and doesn’t fluctuate, unlike other sustainable sources like solar and wind.
These factors make geothermal energy systems considerably better for the environment and provide a practical approach to reducing household carbon footprint. Today, over one million geothermal heat pumps provide heating and cooling solutions worldwide. Thanks to these cost-saving and sustainability benefits, the use rate of these systems is expected to increase by 10% yearly, predominantly in the U.S. and Japan.
Biggest Hurdles to Mass Adoption
There are two main barriers affecting geothermal projects. First is the hefty installation costs, which range from $10,000-$40,000 depending on the system configuration, ground accessibility, plot size and other factors. According to Family Handyman, this makes geothermal systems around 40% more expensive to install than conventional HVAC systems.
However, the energy savings, reduced maintenance and sustainability benefits over the life of the geothermal system means it will pay for itself within a few short years.
The second hurdle is the amount of space required. Few homeowners have ample outdoor space to accommodate large underground geothermal contraptions. To tackle this problem, researchers from University of Minnesota have developed a system that amplifies the capacity of cooling components, reducing the space required for drilling by 95% and improving overall efficiency.
Another solution is district heating and cooling, which captures geothermal energy from a centralized source and distributes it on a community-wide level. This approach can decarbonize the U.S. energy industry and reduce as much as 24,500 miles of grid transmission lines by 2050
Save Energy With Geothermal Heating and Cooling
Despite the intimidating upfront installation cost, the long-term savings and positive environmental impact make geothermal systems a win-win choice.









